Control of Elementary Excitations by Acoustic Fields
Solid-state systems host various fundamental excitations, such as electrons, holes, excitons, and magnons, which are crucial for future electronic and quantum technologies. These excitations are highly sensitive to strain—small changes in the atomic arrangement of a crystal can significantly alter their properties. Phonons, the quanta of lattice vibrations, provide a dynamic source of strain that can be harnessed for precise control of these excitations.
In this CReA, we investigate how elastic vibrations, specifically surface acoustic waves (SAWs) and bulk acoustic waves (BAWs), can manipulate elementary excitations at the nanoscale. Using high-quality materials and advanced nanofabrication techniques, we design structures that efficiently couple to dynamic strain fields. By employing piezoelectric transducers, we generate acoustic waves at frequencies up to 20 GHz, enabling control over material excitations in semiconductor and magnetic systems. Our research spans applications in telecommunications, quantum information processing, and hybrid acousto-opto-electronic systems.
Acoustic control offers a pathway to novel quantum technologies, including tunable exciton-polaritons, spin manipulation in color centers, and magneto-acoustic interactions in ferromagnetic nanostructures. Future breakthroughs could enable coherent transduction between microwave and optical domains, paving the way for advanced quantum networks and next-generation electronic devices.
Scientific Highlights
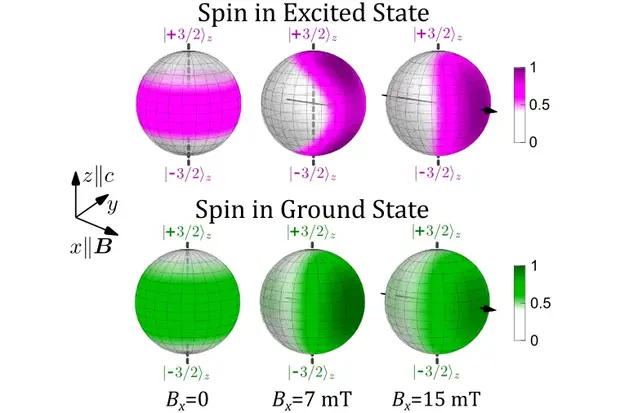
Dynamical reorientation of spin multipoles
A research team led by PDI has shown that weak magnetic fields applied perpendicular to the symmetry axis of the VSi center lead to the inversion of the ODMR contrast for certain spin transitions in both the ground and excited states. The experimental results are well reproduced by a theoretical model introduced in the manuscript, which explains the unusual behavior of the ODMR signal as a consequence of the reorientation of the spin polarization under the transverse magnetic field. More…
Dr. Mingyun Yuan Recognized as an Emerging Leader in JPhysD Special Issue
Dr. Mingyun Yuan has been recognized as an Emerging Leader in a special issue of Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics (JPhysD). This acknowledgment reflects Dr. Yuan’s contributions to the field of applied physics, placing her among a select group of early-career researchers identified for their potential and achievements. More…
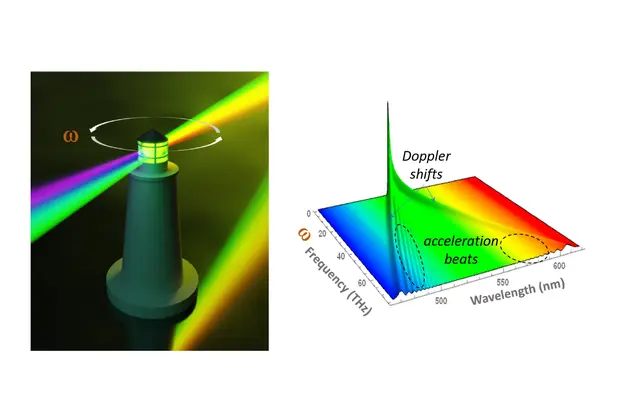
"Acceleration beats” shine bright light on novel universal modulation regime
PDI researchers have discovered a novel modulation regime in semiconductor-based lasers, characterized by "acceleration beats". The universal effect, observed experimentally for the first time, suggests potential for new high-frequency spectral features and quantum control protocols, with implications extending to cosmic and high-energy particle phenomena. More…
Madeleine Msall Honored with Prestigious Appointment at Bowdoin College
We are delighted to announce that PDI guest scientist Madeleine Msall has been named Josiah Little Professor of Natural Sciences at her home faculty, Bowdoin College, Maine. This prestigious recognition highlights her exceptional contributions to science and education at home and abroad. More…
On-chip GHz time crystals with semiconductor photonic devices pave way to new physics and optoelectronic applications
Researchers have observed a time crystal on a microscale semiconductor chip oscillating at a rate of several billion times per second, unveiling exceptionally high non-linear dynamics in the GHz range. The results establish a firm connection between formerly uncorrelated areas of non-linear exciton-polariton dynamics and coherent optomechanics at GHz frequencies. More…
Selected Publications
2025
- GHz acousto-optic angular momentum with tunable topological charge
Authors: A. Pitanti, N. Ashurbekov, I. dePedro-Embid, M. Msall, P. V. Santos
Source: Nat Commun 2025, 16 (1), 8116
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-63362-w
- Thermal Dynamics Induced by Surface Acoustic Waves in Lanthanide-Doped Core@Multishell Nanoparticles
Authors: Pablo B. Pinto, Pedro W. Matrone, Flávia S. Ferreira, Paulo V. Santos, Fernando A. Sigoli, Odilon D. D. Couto Jr.
Source: Advanced Optical Materials 2025, 13 (14), 2403497
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202403497
2024
- Acoustic Modulation of Excitonic Complexes in hBN/WSe2/hBN Heterostructures
Authors: Marcos L. F. Gomes, Pedro W. Matrone, Alisson R. Cadore, Paulo V. Santos, Odilon D. D. Couto Jr.
Source: Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 49, 15517–15524
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c03301
- Solid-State Continuous Time Crystal in a Polariton Condensate with a Built-in Mechanical Clock
Authors: I. Carraro-Haddad, D. L. Chafatinos, A. S. Kuznetsov, I. A. Papuccio-Fernández, A. A. Reynoso, A. Bruchhausen, K. Biermann, P. V. Santos, G. Usaj, A. Fainstein
Source: Science 384, 995 (2024)
DOI: 10.1126/science.adn7087
- Acceleration-Induced Spectral Beats in Strongly Driven Harmonic Oscillators
Authors: A. S. Kuznetsov, K. Biermann, and P. V. Santos
Source: Nat. Commun. 15, 5343 (2024)
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49610-5
- Generation of GHz surface acoustic waves in (Sc,Al)N thin films grown on free-standing polycrystalline diamond wafers by plasma-assisted molecular beam epitaxy
Authors: M. Yuan, D. V. Dinh, S. Mandal, O. A. Williams, Z. Chen, O. Brandt, and P. V. Santos
Source: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57, 495103 (2024)
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/ad76ba
- Dynamical reorientation of spin multipoles in silicon carbide by transverse magnetic fields
Authors: A. Hernández-Mínguez, A. V. Poshakinskiy, M. Hollenbach, P. V. Santos, and G. V. Astakhov
Source: Phys. Rev. Appl. 22, 044021 (2024)
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.22.044021
- Spatial Analysis of Multi-Frequency SAW Beams Excited by Slanted IDTs on ZnO-SiC Heterostructures
Authors: Y.-T. Liou, M. Msall, A. Hernández-Mínguez, and P. V. Santos
Source: J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57, 415302 (2024)
DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/ad600e
2023